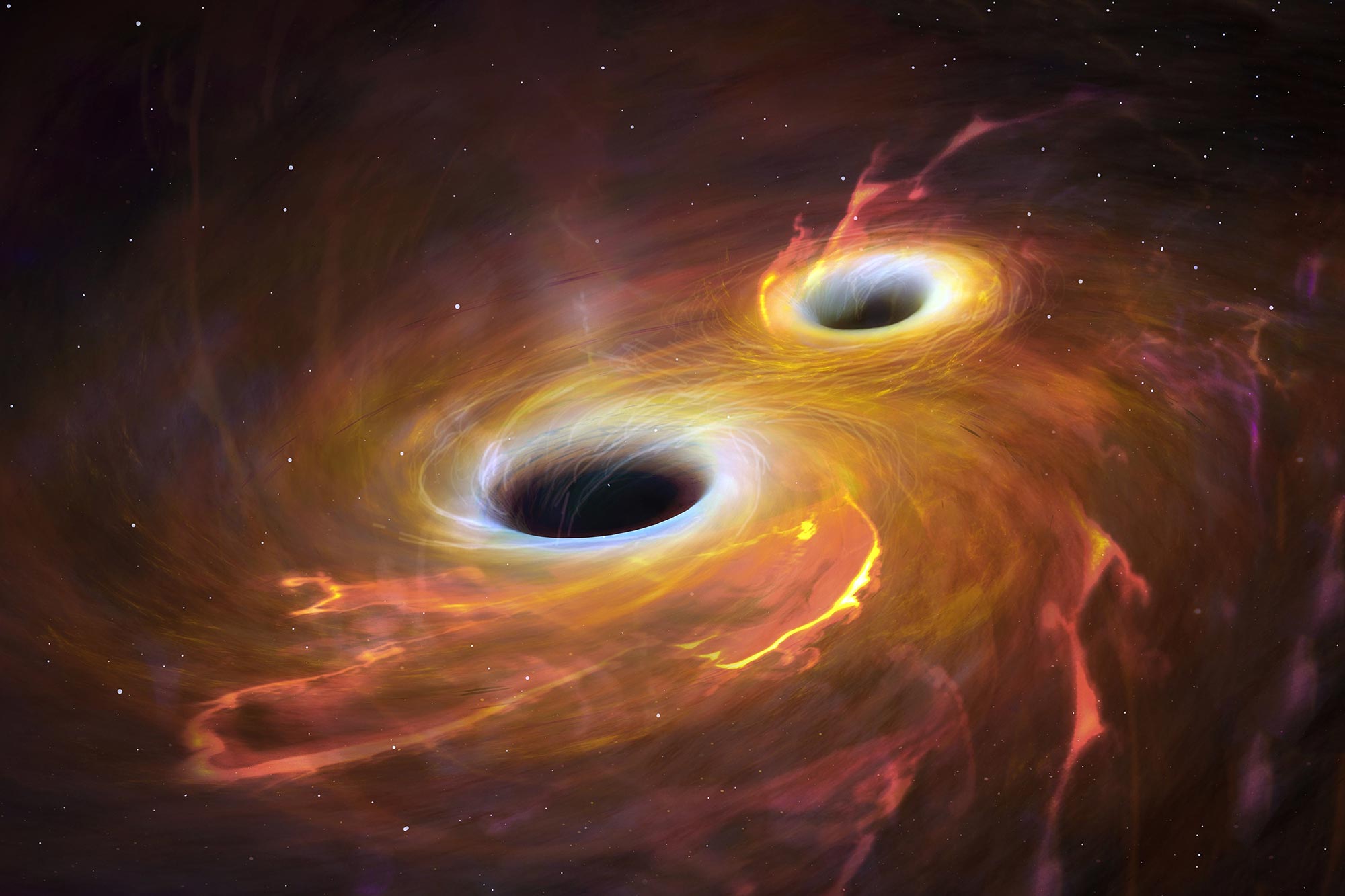
انطباع فنان عن ثقبين أسودين على وشك التصادم.
تكشف الملاحظات والتحليلات الجديدة عن ثقبين أسودين من جالوت لا يفصل بينهما سوى 750 سنة ضوئية ويغلقان ، حيث يدوران حول بعضهما البعض في أعقاب اندماج المجرات.
اكتشف علماء الفلك من معهد فلاتيرون وزملاؤهم اثنين من شبحي جالوت في طريقهما إلى اجتماع كارثي. أعلن علماء الفلك في 9 يناير في اجتماع الجمعية الفلكية الأمريكية في سياتل وفي ورقة بحثية نُشرت في رسائل مجلة الفيزياء الفلكية.
في حين أن الثقوب السوداء الهائلة متقاربة من الناحية الكونية على بعد 750 سنة ضوئية فقط ، فإنها لن تندمج لبضع مئات الملايين من السنين. في غضون ذلك ، يوفر اكتشاف علماء الفلك تقديرًا أفضل لعدد الثقوب السوداء الهائلة التي تقترب أيضًا من الاصطدام في الكون.

يُظهر تصور هذا الفنان اندماج مجري في مرحلة متأخرة وثقبين أسودين مركزيين تم اكتشافهما حديثًا. الثقوب السوداء الثنائية هي الأقرب معًا التي لوحظت في أطوال موجية متعددة. الائتمان: ALMA (ESO / NAOJ / NRAO) ؛ إم. وايس (NRAO / AUI / NSF)
سيساعد هذا العدد المحسن للرؤوس العلماء في الاستماع إلى جوقة الكون الممتدة من التموجات الشديدة في الزمكان والمعروفة باسم[{” attribute=””>gravitational waves, the largest of which are products of supermassive black holes close to collision in the aftermath of galaxy mergers. Detecting that gravitational-wave background will improve estimates of how many galaxies have collided and merged in the universe’s history.
The short distance between the newly discovered black holes “is fairly close to the limit of what we can detect, which is why this is so exciting,” says study co-author Chiara Mingarelli, an associate research scientist at the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Astrophysics in New York City.
Due to the small separation between the black holes, the astronomers could only differentiate between the two objects by combining many observations from seven telescopes, including NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. (Although supermassive black holes aren’t directly visible through an optical telescope, they are surrounded by bright bunches of luminous stars and warm gas drawn in by their gravitational pull.)

Telescope observations of two newly discovered supermassive black holes on a collision course. Their host galaxy, left, is a mash-up of two galaxies that have collided. The pink box shows the location of the supermassive black holes. Close observation of the pair, right, reveals two distinct black holes (white spots) only 750 light-years apart. Credit: M.J. Koss et al.
The astronomers found the pair quickly once they started looking, which means that close-together supermassive black holes “are probably more common than we think, given that we found these two and we didn’t have to look very far to find them,” Mingarelli says.
The newly identified supermassive black holes inhabit a mash-up of two galaxies that collided around 480 million light-years away from Earth. Gargantuan black holes live in the heart of most galaxies, growing bigger by gobbling up surrounding gas, dust, stars, and even other black holes. The two supermassive black holes identified in this study are true heavyweights: They clock in at 200 million and 125 million times the mass of our sun.
The black holes met as their host galaxies smashed into each other. Eventually they will begin circling each other, with the orbit tightening as gas and stars pass between the two black holes and steal orbital energy. Ultimately the black holes will start producing gravitational waves far stronger than any that have previously been detected, before crashing into each other to form one jumbo-size black hole.
https://www.youtube.com/watch؟v=gSSa_u_EOnY
يُظهر تصور هذا الفنان اندماج مجري في مرحلة متأخرة وثقبين أسودين مركزيين تم اكتشافهما حديثًا. الثقوب السوداء الثنائية هي الأقرب معًا التي لوحظت في أطوال موجية متعددة. ائتمان:[{” attribute=””>ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), M. Koss et al (Eureka Scientific), S. Dagnello (NRAO/AUI/NSF)
Prior observations of the merging galaxies saw only a single supermassive black hole: Because the two objects are so close together, scientists couldn’t definitively tell them apart using a single telescope. The new survey, led by Michael J. Koss of Eureka Scientific in Oakland, California, combined 12 observations made on seven telescopes on Earth and in orbit. Although no single observation was enough to confirm their existence, the combined data conclusively revealed two distinct black holes.
“It’s important that with all these different images, you get the same story — that there are two black holes,” says Mingarelli, when comparing this new multi-observation research with previous efforts. “This is where other studies [of close-proximity supermassive black holes] سقطوا في الماضي. عندما تبعهم الناس ، اتضح أن هناك ثقبًا أسودًا واحدًا فقط. [This time we] العديد من الملاحظات ، جميعها متفقة “.

تمثيل تخطيطي لأهم المراحل والآليات الفيزيائية الحرجة التي تقود اندماج اثنين من الثقوب السوداء الهائلة والوقت التمثيلي المقابل والمقاييس المكانية. الائتمان: José Utreras / Ezequiel Treister ، مركز الفيزياء الفلكية والتقنيات المرتبطة (CATA) ؛ مايكل كوس (يوريكا العلمية) وآخرون.
استخدمت هي وعالم معهد فلاتيرون الزائر أندرو كيسي كلايد الملاحظات الجديدة لتقدير عدد سكان الكون من الثقوب السوداء الهائلة المندمجة ، ووجدوا أنه “قد يكون مرتفعًا بشكل مدهش” ، كما يقول مينجاريللي. يتنبأون بوجود وفرة من أزواج الثقوب السوداء فائقة الكتلة ، مما يولد كمية كبيرة من موجات الجاذبية فائقة القوة. يجب أن يؤدي كل هذا الصخب إلى خلفية موجات جاذبية عالية يسهل اكتشافها مما لو كان التعداد السكاني أصغر. يقول مينجاريللي إن أول اكتشاف على الإطلاق للثرثرة الخلفية لموجات الجاذبية قد يأتي “قريبًا جدًا”.
المرجع: “UGC 4211: نواة مجرة نشطة مزدوجة مؤكدة في الكون المحلي عند 230 قطعة من الفصل النووي” بقلم مايكل ج. بيني تراختنبروت ، وفرانز إي باور ، وجورج سي بريفون ، وكلاوديو ريتشي ، وريتشارد موشوتسكي ، ولوريتو باركوس-مونوز ، ولورا بليشا ، وتوماس كونور ، وفيونا هاريسون ، وتينجتينج ليو ، وماكون ماجنو ، وكيارا إم إف مينجاريللي ، وفرانشيسكو مولر-سانشيز ، وكيوسوك أوه ، تارو شيميزو ، كريستا لين سميث ، دانيال ستيرن ، ميغيل بارا تيلو وسي ميجان أوري ، 9 يناير 2023 ، رسائل مجلة الفيزياء الفلكية.
DOI: 10.3847 / 2041-8213 / aca8f0

“هواة الإنترنت المتواضعين بشكل يثير الغضب. مثيري الشغب فخور. عاشق الويب. رجل أعمال. محامي الموسيقى الحائز على جوائز.”