
استخدم الباحثون المحاكاة لاستكشاف الشبكة الكونية ، النمط الخيطي للمجرات الموجود على نطاقات كبيرة في جميع أنحاء الكون. من خلال معالجة توزيع المجرات كمجموعة من النقاط وتطبيق التقنيات الرياضية المطورة لعلوم المواد ، فقد قاموا بتحديد الاضطراب النسبي للكون واكتسبوا فهمًا أفضل لبنيته الأساسية. الائتمان: ناسا / جامعة شيكاغو ومتحف أدلر القبة السماوية والفلك
الكون مليء بالمجرات ، والتي تظهر على المقاييس الكبيرة نمطًا خيطيًا ، يشار إليه باسم الشبكة الكونية. هذا التوزيع غير المتجانس للمواد الكونية هو في بعض النواحي مثل العنب البري في كعكة حيث تتجمع المواد في مناطق معينة ولكنها قد تكون مفقودة في مناطق أخرى.
استنادًا إلى سلسلة من عمليات المحاكاة ، بدأ الباحثون بسبر البنية غير المتجانسة للكون من خلال معالجة توزيع المجرات على أنها مجموعة من النقاط – مثل الجسيمات الفردية للمادة التي تشكل مادة – وليس كتوزيع مستمر. مكنت هذه التقنية من تطبيق الرياضيات المطورة لعلم المواد لتحديد الاضطراب النسبي للكون ، مما يتيح فهمًا أفضل لبنيته الأساسية.

تصور لأكبر الهياكل في الكون من مسح سلون الرقمي للسماء. الائتمان: ناسا / جامعة شيكاغو ومتحف أدلر القبة السماوية والفلك
أوضح أوليفر فيلكوكس ، مؤلف مشارك في الدراسة: “ما وجدناه هو أن توزيع المجرات في الكون يختلف تمامًا عن الخصائص الفيزيائية للمواد التقليدية ، التي لها توقيعها الفريد”.
تم نشر هذا العمل الآن في مراجعة البدنية X، سالفاتور توركواتو ، عضو وزائر متكرر في معهد الدراسات المتقدمة وأستاذ العلوم الطبيعية لويس برنارد ومقره في[{” attribute=””>Princeton University’s departments of chemistry and physics; and Oliver Philcox a visiting Ph.D. student at the Institute from September 2020 to August 2022, now a Junior Fellow in the Simons Society of Fellows, hosted at Columbia University.
https://www.youtube.com/watch؟v=ZI0ncxCG6qw
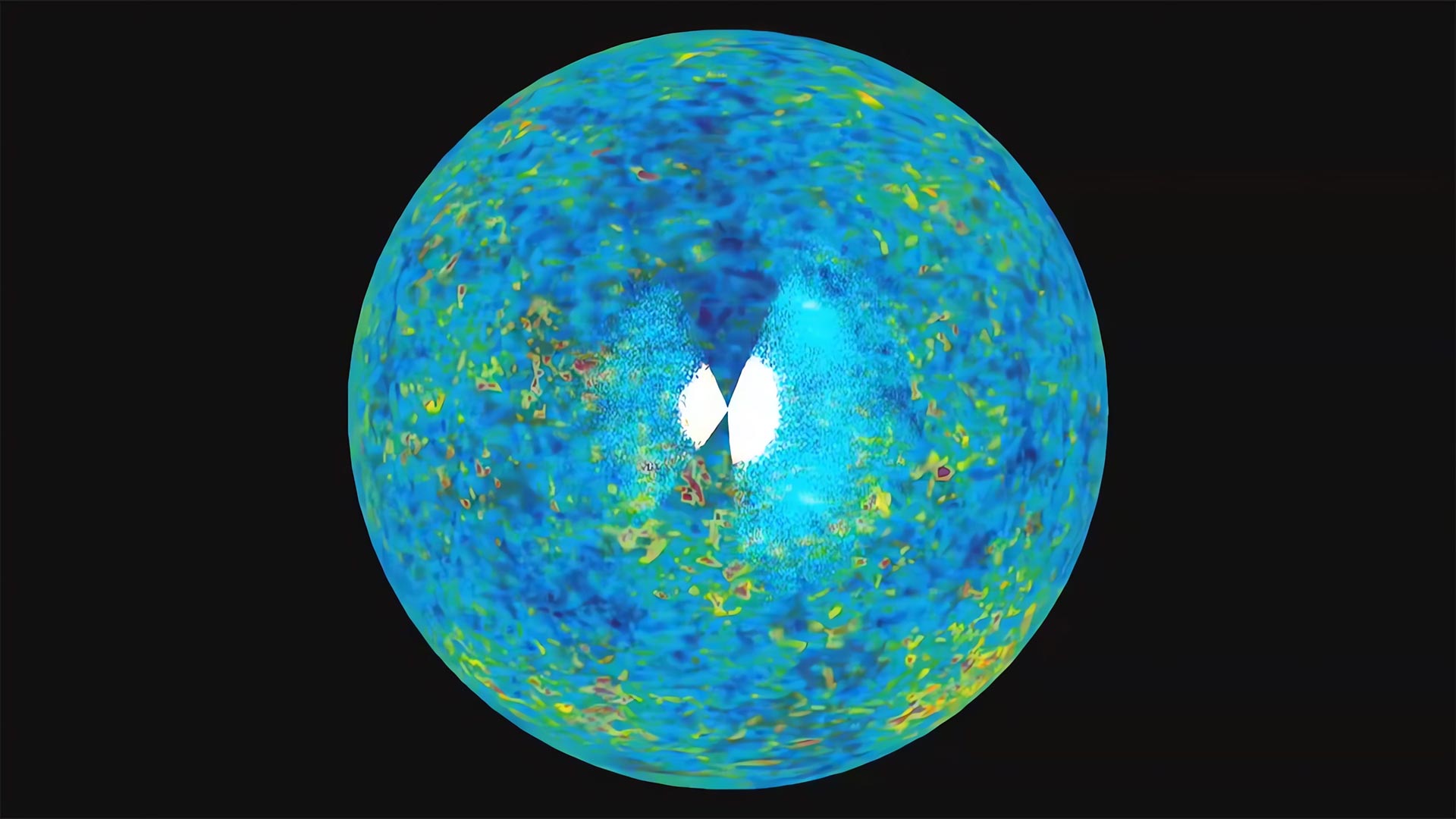
يقدم هذا التصور عرضًا ثلاثي الأبعاد لأكبر الهياكل في الكون. يبدأ ببيانات من مسح Sloan Digital Sky ويصغر ليكشف عن بيانات من WMAP. ائتمان:[{” attribute=””>NASA/University of Chicago and Adler Planetarium and Astronomy Museum
The pair analyzed public simulation data generated by Princeton University and the Flatiron Institute. Each of the 1,000 simulations consists of a billion dark matter “particles,” whose clusters, formed by gravitational evolution, serve as a proxy for galaxies.
One of the main results of the paper concerns the correlations of pairs of galaxies that are topologically connected to one another by means of the pair-connectedness function. Based on this—and the array of other descriptors that arise in the theory of heterogeneous media—the research team showed that on the largest scales (on the order of several hundred megaparsecs), the universe approaches hyperuniformity, while on smaller scales (up to 10 megaparsecs) it becomes almost antihyperuniform and strongly inhomogeneous.

A section of the universe (black and white), with dark matter halos indicated by points and their associated large-scale topological structures indicated by colors. Credit: Philcox & Torquato; The Quijote Simulations
“The perceived shift between order and disorder depends largely on scale,” stated Torquato. “The pointillist technique of Georges Seurat in the painting A Sunday on La Grande Jatte (see image below) produces a similar visual effect; the work appears disordered when viewed up-close and highly ordered from afar. In terms of the universe, the degree of order and disorder is more subtle, as with a Rorschach inkblot test that can be interpreted in an infinite number of ways.”

“A Sunday on La Grande Jatte” by Georges Seurat.
Statistical tools, specifically nearest-neighbor distributions, clustering diagnostics, Poisson distributions, percolation thresholds, and the pair-connectedness function, allowed the researchers to develop a consistent and objective framework for measuring order. Therefore, their findings, while made in a cosmological context, translate to a number of other dynamical, physical systems.
This interdisciplinary work, combining the techniques of cosmology and condensed matter physics, has future implications for both fields. Beyond the distribution of galaxies, many other features of the universe can be explored with these tools, including cosmic voids and the ionized hydrogen bubbles that formed during the reionization phase of the universe. Conversely, the novel phenomena discovered about the universe may also provide insight into various material systems on Earth. The team recognizes that more work will be needed before these techniques can be applied to real data, but this work provides a strong proof-of-concept with significant potential.
Reference: “Disordered Heterogeneous Universe: Galaxy Distribution and Clustering across Length Scales” by Oliver H. E. Philcox and Salvatore Torquato, 14 March 2023, Physical Review X.
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevX.13.011038

“هواة الإنترنت المتواضعين بشكل يثير الغضب. مثيري الشغب فخور. عاشق الويب. رجل أعمال. محامي الموسيقى الحائز على جوائز.”



.jpg)
