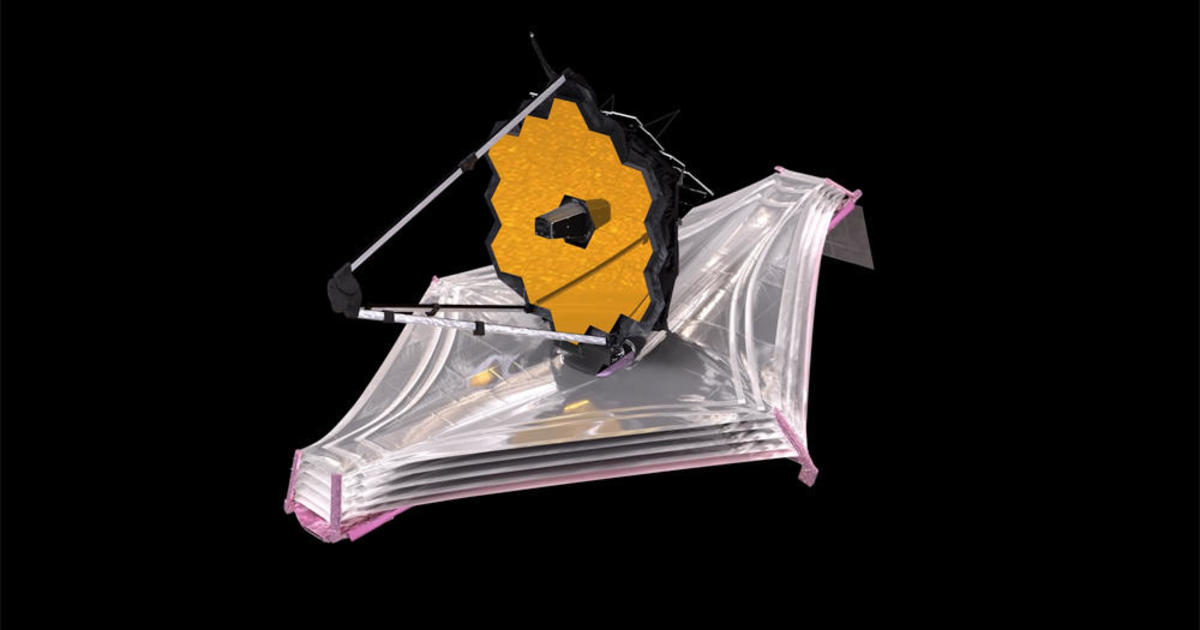
في 1 يوليو 2023 ، تم إطلاق المركبة الفضائية إقليدس ، التي تديرها وكالة الفضاء الأوروبية (ESA) ، بنجاح على صاروخ SpaceX Falcon 9 من محطة كيب كانافيرال للقوة الفضائية. تهدف المركبة الفضائية إلى استكشاف المكونات الغامضة للكون والمادة المظلمة والطاقة المظلمة. الائتمان: SpaceX
انطلقت المركبة الفضائية Euclid التابعة لوكالة الفضاء الأوروبية ESA على متن صاروخ SpaceX Falcon 9 من محطة كيب كانافيرال للقوة الفضائية في فلوريدا ، الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية ، الساعة 11:12 صباحًا[{” attribute=””>EDT on July 1, 2023. The successful launch marks the beginning of an ambitious mission to uncover the nature of two mysterious components of our Universe: dark matter and dark energy, and to help us answer the fundamental question: what is the Universe made of?
Following launch and separation from the rocket, ESA’s European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Darmstadt, Germany, confirmed acquisition of signal from Euclid via the New Norcia ground station in Australia at 17:57 CEST (11:57 a.m. EDT).
https://www.youtube.com/watch؟v=wbWA1OhHeCA
تم إطلاق المركبة الفضائية Euclid التابعة لوكالة الفضاء الأوروبية (ESA) بنجاح في 1 يوليو 2023 ، للكشف عن طبيعة المادة المظلمة والطاقة المظلمة في الكون. ستنشئ خريطة ثلاثية الأبعاد دقيقة للكون من خلال مراقبة بلايين المجرات واستخدام أدوات علمية متقدمة لتحليل هذه المجرات. ومن المقرر أن تستمر المهمة ست سنوات وستقدم مسحًا غير مسبوق للسماء. ائتمان:[{” attribute=””>SpaceX
“The successful launch of Euclid marks the beginning of a new scientific endeavor to help us answer one of the most compelling questions of modern science,” says ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher. “Euclid has been made possible by ESA’s leadership, the effort and expertise of hundreds of European industrial and scientific institutions, and through collaboration with international partners. The quest to answer fundamental questions about our cosmos is what makes us human. And, often, it is what drives the progress of science and the development of powerful, far-reaching, new technologies. ESA is committed to expanding Europe’s ambitions and successes in space for future generations.”

On July 1, 2023, at 11:12 a.m. EDT, ESA’s latest astrophysics mission, Euclid, lifted off on a Space X Falcon 9 from Cape Canaveral in Florida, USA. Euclid has now started its month-long journey to Sun-Earth Lagrange point L2, located 1.5 million kilometers from Earth, in the opposite direction from the Sun. Credit: ESA – S. Corvaja
“The Euclid mission is the result of the passion and expertise of those who contributed to designing and building this sophisticated space telescope, the competence of our flight operations team, and the inquiring spirit of the science community,” says Giuseppe Racca, ESA’s Euclid Project Manager. “There have been many challenges during the project, but we have worked hard and now we have successfully reached this launch milestone together with our partners in the Euclid Consortium and NASA.”
The Euclid Consortium contributed the two highly advanced scientific instruments – the visible-wavelength camera (VIS) and the Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP). NASA provided the detectors for NISP.

ESA’s Euclid will examine visible and infrared light from distant galaxies using two scientific instruments on board. These instruments will measure the accurate position and shapes of galaxies in visible light, and their redshift (from which their distance can be derived) in the infrared light. With these data, scientists can construct a 3D map of the distributions of both the galaxies and the dark matter in the Universe. The map will show how large-scale structure evolved over time, tracing the role of dark energy.
The VISible instrument (VIS) takes very sharp images of galaxies over a much larger fraction of sky than would be possible from the ground. These observations will be used to measure the shapes of over a billion galaxies.
As the name suggests, VIS collects visible light. It is sensitive to wavelengths from green (550 nanometres) up to near infrared (900 nm). The instrument uses a mosaic of 36 CCDs (Charge Coupled Devices, a type of camera sensor), each of which contains more than 4000 pixels by 4000 pixels. This gives the detector a total of about 600 megapixels, equivalent to almost seventy 4K resolution screens.
Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) is dedicated to making spectroscopic measurements of galaxies, which involves determining how much light they emit per wavelength. This is useful for measuring the galaxies’ redshift, which cosmologists can use to estimate the distance to each galaxy. NISP has the largest field of view for an infrared instrument ever flown in space. The instrument measures near-infrared light (900–2000 nm) using a grid of 16 detectors, each containing more than 2000 by 2000 pixels.
Credit: ESA
Exploring the dark Universe
Euclid will observe billions of galaxies out to 10 billion light-years to create the largest, most accurate 3D map of the Universe, with the third dimension representing time itself. This detailed chart of the shape, position, and movement of galaxies will reveal how matter is distributed across immense distances and how the expansion of the Universe has evolved over cosmic history, enabling astronomers to infer the properties of dark energy and dark matter. This will help theorists to improve our understanding of the role of gravity and pin down the nature of these enigmatic entities.
“Today we celebrate the successful launch of a ground-breaking mission that places Europe at the forefront of cosmological studies,” says Carole Mundell, ESA’s Director of Science. “If we want to understand the Universe we live in, we need to uncover the nature of dark matter and dark energy and understand the role they played in shaping our cosmos. To address these fundamental questions, Euclid will deliver the most detailed map of the extra-galactic sky. This inestimable wealth of data will also enable the scientific community to investigate many other aspects of astronomy, for many years to come.”
https://www.youtube.com/watch؟v=GhJFvtvgwmc
تم تصميم مهمة Euclid من ESA للكشف عن خصائص وتأثيرات المادة المظلمة والطاقة المظلمة المراوغة ، وهي كيانات يعتقد أنها تهيمن على تكوين الكون ولكنها تظل غير مكتشفة مباشرة. سينشئ إقليدس خريطة ثلاثية الأبعاد للكون ، مستخدماً الوقت كبعد ثالث له ، من خلال مراقبة بلايين المجرات التي تصل إلى 10 مليارات سنة ضوئية. سيساعد هذا التعيين الشامل العلماء على رسم موقع وسرعة المجرات عبر مسافات شاسعة وعبر التاريخ الكوني ، مما يلقي الضوء على توسع الكون بمرور الوقت. الائتمان: ESA
لتحقيق هدفه العلمي الطموح ، تم تجهيز إقليدس بتلسكوب عاكس بطول 1.2 متر يغذي الأداتين العلميتين المبتكرتين: VIS ، التي تلتقط صورًا شديدة الوضوح للمجرات على جزء كبير من السماء ، و NISP ، التي يمكنها تحليل الأشعة تحت الحمراء للمجرات. الضوء بطول الموجة لتحديد المسافة بينهما بدقة.
سيتم التحكم في المركبات الفضائية والاتصالات من ESOC. للتعامل مع الكميات الهائلة من البيانات التي سيحصل عليها Euclid ، تمت ترقية شبكة Estrack الخاصة بهوائيات الفضاء السحيق التابعة لوكالة الفضاء الأوروبية. سيتم تحليل هذه البيانات من قبل Euclid Consortium – وهي مجموعة تضم أكثر من 2000 عالم من أكثر من 300 معهد في جميع أنحاء أوروبا والولايات المتحدة وكندا واليابان.

بالنسبة لبعثات وكالة الفضاء الأوروبية الأخرى ، تصل بيانات المركبات الفضائية إلى مركز العمليات الفضائية الأوروبية (ESOC) التابع لوكالة الفضاء الأوروبية (ESOC) في ألمانيا ، عبر محطات أرضية في جميع أنحاء العالم.
يتم إرسال البيانات الأولية إلى المركز الأوروبي لعلم الفلك الفضائي (ESAC) في إسبانيا. من ESAC ، يتم توزيع البيانات على مراكز المعالجة الخاصة بقطاع العلوم الأرضية التابع لاتحاد إقليدس ، ومقره في عدد من الدول الأوروبية والولايات المتحدة الأمريكية.
اتحاد إقليدس (EC) هو منظمة تضم أكثر من 2000 باحث في الفيزياء النظرية والفيزياء الفلكية وعلم الفلك الفضائي والمهندسين والفنيين والموظفين الإداريين. تم اختياره من قبل وكالة الفضاء الأوروبية ليكون الاتحاد العلمي الرسمي الوحيد المسؤول عن الأدوات العلمية وإنتاج البيانات وقيادة الاستغلال العلمي للبعثة حتى الانتهاء.
الجزء الأرضي للعلوم EC مسؤول عن تصميم واختبارات التطوير والتكامل وتشغيل أدوات معالجة البيانات وخطوط الأنابيب ومراكز البيانات. تشمل منتجات البيانات المعالجة صورًا وأطيافًا مُعايرة ، وكتالوجات للقياسات العلمية ، وتوثيقًا.
على فترات منتظمة ، سيتم إتاحة كنز بيانات إقليدس المعالجة للجمهور للجمهور عبر أرشيف علم الفلك في ESAC. من ESAC يتم التخطيط للعمليات العلمية ، حيث يتم أرشفة جميع البيانات العلمية التي تنتجها بعثة ESA وإتاحتها للعالم.
الائتمان: ESA
مع تقدم المهمة ، سيتم إصدار كنز إقليدس من البيانات بإيقاع سنوي وسيكون متاحًا للمجتمع العلمي العالمي من خلال الأرشيف العلمي الذي يستضيفه المركز الأوروبي لعلم الفلك الفضائي التابع لوكالة الفضاء الأوروبية في إسبانيا.
يقول رينيه لوريج ، عالم مشروع إقليدس في وكالة الفضاء الأوروبية: “هذه لحظة عظيمة للعلم ، لحظة نتطلع إليها منذ فترة طويلة: إطلاق إقليدس ، في مهمة لفك لغز المادة المظلمة والطاقة المظلمة”. “اللغز الكبير للمكونات الأساسية للكون يحدق بنا في وجوهنا ، ويقدم تحديا هائلا. بفضل تلسكوبه المتقدم وأدواته العلمية القوية ، يستعد إقليدس لمساعدتنا في كشف هذا اللغز “.

سيدور إقليدس التابع لوكالة الفضاء الأوروبية حول نقطة لاغرانج الثانية (L2) ، على بعد 1.5 مليون كيلومتر من الأرض في الاتجاه المعاكس للشمس. L2 هي نقطة توازن لنظام الشمس والأرض الذي يتبع الأرض حول الشمس.
في مداره في L2 ، يمكن لواقي الشمس لإقليدس دائمًا حجب الضوء من الشمس والأرض والقمر أثناء توجيه تلسكوبه نحو الفضاء السحيق ، مما يضمن مستوى عالٍ من الاستقرار لأجهزته.
في L2 ، ينضم إقليدس إلى مهمة Gaia التابعة لوكالة الفضاء الأوروبية ESA و ESA / NASA / CSA James Webb Space Telescope ، اللذان يدوران أيضًا حول نقطة التوازن هذه ، كل منها يتبع مسارات منفصلة جيدًا.
الائتمان: ESA
رحلة إلى لاجرانج بوينت 2
في الأسابيع الأربعة المقبلة ، سوف يسافر إقليدس نحو نقطة لاغرانج 2 من الشمس والأرض ، وهي نقطة توازن لنظام الشمس والأرض تقع على بعد 1.5 مليون كيلومتر من الأرض (حوالي أربعة أضعاف المسافة بين الأرض والقمر) في الاتجاه المعاكس للشمس. هناك ، سيتم مناورة إقليدس في مدار حول هذه النقطة وسيبدأ مراقبو المهمة الأنشطة للتحقق من جميع وظائف المركبة الفضائية ، والتحقق من التلسكوب وتشغيل الأدوات العلمية في النهاية.
سيشارك العلماء والمهندسون بعد ذلك في مرحلة مكثفة مدتها شهران لاختبار ومعايرة أدوات إقليدس العلمية والتحضير للملاحظات الروتينية. على مدار ست سنوات ، سيقوم إقليدس بمسح ثلث السماء بشكل غير مسبوق[{” attribute=””>accuracy and sensitivity.

ESA’s Euclid mission is a highly ambitious project undertaken by the European Space Agency (ESA) to investigate and understand the nature of two enigmatic components of our Universe: dark matter and dark energy. Launched on July 1, 2023, the spacecraft will observe billions of galaxies up to 10 billion light-years away to construct the most accurate 3D map of the Universe ever made. Credit: ESA
About Euclid
Euclid is a European mission, built and operated by ESA, with contributions from NASA. The Euclid Consortium is responsible for providing the scientific instruments and scientific data analysis. ESA selected Thales Alenia Space as prime contractor for the construction of the satellite and its service module, with Airbus Defence and Space chosen to develop the payload module, including the telescope. NASA provided the detectors of the Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer, NISP. Euclid is a medium-class mission in ESA’s Cosmic Vision Programme.

“هواة الإنترنت المتواضعين بشكل يثير الغضب. مثيري الشغب فخور. عاشق الويب. رجل أعمال. محامي الموسيقى الحائز على جوائز.”